View 的绘制 - Measure 流程
在说 Measure 过程之前,需要解释几个概念。 MeasureSpec 和 SpecMode
MeasureSpec
- MeasureSpec很大程度上决定了 View 的尺寸规格,之所以很大程度上,是因为这个过程还受到父容器的影响,在测量过程中,系统会将 View 的 LayoutParams ,根据父容器的所施加的规则转换成对应的 MeasureSpce ,然后再根据这个 MeasureSpce 测量出 View 的宽高。
- MeasureSpce代表一个 32 位的 int 值,高 2 位代表 SpecMode ,即测量模式,低 30 位代表 SpecSize ,即某种测量模式下的规格大小。
- MeasureSpec通过打包把 SpecMode 和 SpecSize 组成一个 int 值从而避免过多的对象内存分配,同时提供打包和解包的方法,从而得到原始的 SpecMode 和SpecSize
SpecMode
分三种模式:
- UNSPECIFIED 父容器不对子 View 做任何限制,要多大给多大,一般用于系统内部,表示一种测量状态
- EXACTLY 父容器已经检测出子 view 所需要的大小,这个时候 View 的最终大小就是 specSize 所指的值,对应于 LayoutParams 中的 match_parent 和具体的数值这两种模式
- AT_MOST 父容器指定了一个可用大小即 SpecSize , View 大小不能大于这个值,具体是什么值要看不同 View 的具体实现,它对应了 Layoutparams 中的warp_content
SpecSize
某种模式的规格大小。是一个值。
MeasureSpce 与 LayoutParams 关系
MeasureSpce 不是唯一由 LayoutParams 决定的, LayoutParams 需要和父容器一起才能决定 View 的 MeasureSpce ,从而进一步决定 View 的宽高。对应顶级View(DecorView)和普通的 View , MeasureSpce 的转换略有不同,
- DecorView: 其 MeasureSpce 由窗口的尺寸和自身的 LayoutParams 共同决定
- 普通View: 其 MeasureSpce 由父容器的 MeasureSpce 和自身的 LayoutParams 共同决定。概况起来就是: 子 View 的MeasureSpec = LayoutParams + margin + padding + 父容器的MeasureSpec
DecorView 的 MeasureSpce 创建过程
上一篇我们知道。在 performTraversals() 会执行 measureHierarchy() 。在 measureHierarchy() 会创建到 DecorView 的 MeasureSpce,关键代码如下。
//ViewRootImpl # measureHierarchy()
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
接下来看 getRootMeasureSpec() 的代码
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
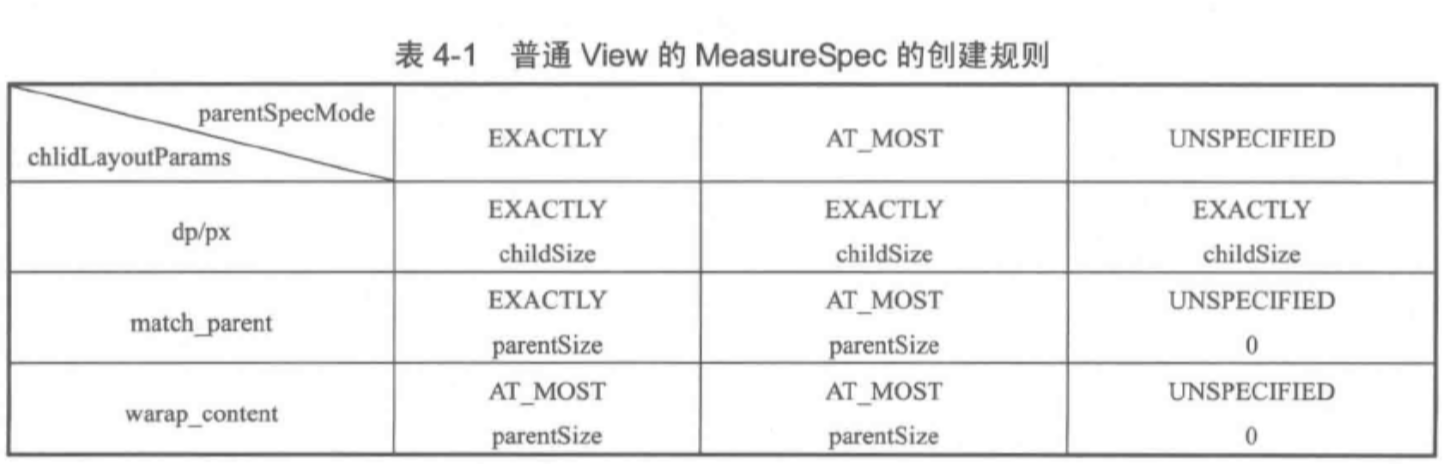
通过上述代码, DecorView 的 MeasureSpec 的产生过程就很明确了,具体来说就是遵守如下规则。根据 layouParams 的宽高的参数来划分,
- LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT : EXACTLY 精确模式,大小就是窗口的大小
- LayoutParams.WARP_CONTENT : AT_MOST (最大模式) 大小不确定,但是不能 超过窗口的大小
- 固定大小(写死的值),EXACTLY(精确模式),大小就是当前写死的数值
普通 View 的 MeasureSpace 创建过程
DecorView 是顶级的 View ,同时也是一个 ViewGroup ,普通的 View 在 measure() 的时候。会根据父容器 MeasureSpec 同时结合 View 本身的 LayoutParams 来确定该 View 的 MeasureSpec ,该 View 的 MeasureSpec 的创建与父容器的 MeasureSpec 和本身的 LayoutParams 有关,此外还和 View 的 margin 和 padding 有关。
这个主要是在ViewGroup # getChildMeasureSpec()中执行的。代码如下。
//spec为父容器的 MeasureSpec padding 子 View 的 padding , childDimension 子 View 想要的宽度/高度
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding , int childDimension) {
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);//父容器的specMode
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);//父容器的specSize
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {//根据父容器的specMode
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
虽然代码很长,但是很好理解,
- 如果子布局的 LayoutParams 是具体的值,那么子布局的 MeasureSpce 是 EXACTLY ,子布局的可用大小是自己的 LayoutParams 设置的的大小
- 如果子布局设置的 match_parent ,那么子布局的 MeasureSpce 是和父布局的一样,大小就是父布局可用的大小, UNSPECIFIED 除外,这种情况下为0
- 如果子布局设置的是 warp_conent ,那么子布局的 MeasureSpce 就是 AT_MOST ,可用大小就是父布局最大的可用大小, UNSPECIFIED 除外,这种情况下还是 UNSPECIFIED ,并且可用大小为0
换成表格形式就是如下。
MeasureSpce一旦确定, onMeasure() 中就可以得到 View 的测量宽和高
我们就从此继续分析。 Hierarchy 层级,阶层,等级制度。 measureHierarchy() 用于测量整个控件树,
measureHierarchy()
//ViewRootImpl.java
private boolean measureHierarchy(final View host, final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, final Resources res ,
final int desiredWindowWidth , final int desiredWindowHeight) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;
boolean goodMeasure = false;
if (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
//在大屏幕上,我们不希望允许对话框拉伸以填充整个屏幕宽度以显示一行文本。 首先尝试以较小的尺寸进行布局,看看是否适合。
final DisplayMetrics packageMetrics = res.getDisplayMetrics();
res.getValue(com.android.internal.R.dimen.config_prefDialogWidth, mTmpValue , true);
int baseSize = 0;
if (mTmpValue.type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) {
baseSize = (int) mTmpValue.getDimension(packageMetrics);
}
if (baseSize != 0 && desiredWindowWidth > baseSize) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if ((host.getMeasuredWidthAndState() & View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0) {
goodMeasure = true;
} else {
// Didn't fit in that size... try expanding a bit.
baseSize = (baseSize + desiredWindowWidth) / 2;
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if ((host.getMeasuredWidthAndState() & View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0) {
goodMeasure = true;
}
}
}
}
// 如果 goodMeasure 这个变量为 true 的时候,
//(host.getMeasuredWidthAndState() & View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0 是成立的
// 刚开始计算 DecorView 的时候,是不等于 0 的,所以第一次执行 measureHierarchy 方法的时候,
// goodMeasure 为 false ,也就是执行到了下面的 if 语句
if (!goodMeasure) {//DecorView,宽度基本都为match_parent
//创建measureSpec
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth() || mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight()) {
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
return windowSizeMayChange;
}
MeasureHierarchy()有自己的测量方法,会先以较小的尺寸进行布局。让窗口更加优雅(主要是针对 wrap_content 的Dialog),所以设置了 wrap_content 的 Dialog ,有可能执行多次测量 通过 getRootMeasureSpec() 计算出来 MeasureSpce 之后,就执行 performMeasure() 方法,
performMeasure()
//ViewRootImpl.java
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
该方法很简单,就是直接调用mView.measure()方法,而这个 mView 就是执行 setView 方法中,传递过来的 View 。
measure 过程分为两种:
- 只有一个原始的 View ,那么通过 measure() 方法就可以完成了
- 是一个 ViewGroup ,除了完成自己是测量过程,还要遍历调用子 View 的 measure 过程。各个子 View 在递归调用这个流程
针对这两种情况分别讨论。先说 View 的 measure()
View 的 measure 过程
View # measure()
关键代码如下。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
final boolean isExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(mOldWidthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(mOldHeightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean matchingSize = isExactly && getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
&& getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
//仅当给与的 MeasureSpec 发生变化时,或要求强制重新布局时,才会进行测量。
if (forceLayout|| !matchingSize && (widthMeasureSpec !=mOldWidthMeasureSpec
|| heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec)) {
...
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
long logTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
} else {
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
...
}
}
由代码可知:
- 该方法定义的是 final 类型的,子类不能重写该方法
- 仅当给与的 MeasureSpec 发生变化时,或要求强制重新布局时,才会进行测量。 当子控件内容发生变化时,从子控件到父控件会回溯到 ViewRootImpl ,并依次调用父控件的 requestLayout() 方法, requestLayout() 会在 mPrivateFlage 中加入标记 PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT ,从而使这些父控件的 measure() 方法得到顺利执行,进而这个子控件有机会进行重新布局与测量,这便是强制重新布局的意义所在。
- view.measure()方法其实没有实现任何测量的算法,它的作用在于判断是否需要引发 onMeasure() 的调用,并对 onMeasure() 行为的正确性进行检查。
接下来看 onMeasure() 方法,这个方法我们就比较熟悉了,自定义控件的时候经常会被复写的三个方法之一。
View # onMeasure()
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
代码很简单,通过 setMeasureDimension() 设置 View 的宽和高,那么我们就首先看看宽和高是怎么得到的,这就需要查看 getDefaultSize() 方法了
View # getDefaultSize()
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
从 getDefaultSize() 方法的实现来看,分两种情况:
- 对于 AT_MOST 和 EXACTLY 这两种情况, View 的高度是由 specSize 决定的,简单来说,就是 getDefautlSize() 返回的就是 MeasureSpce 对应的 specSize 。
注意:如果我们直接继承 View 的自定义控件,需要重写 onMeasure 方法并设置 wrap_content 时自身大小,否则布局中使用 wrap_content 就相当于使用 match_parent 。
因为 View 使用了 wrap_content ,那么他的 MeasureSpec 就是 AT_MOST ,在这种模式下,他的宽高等于 specSize ,由上面 ViewGroup # getChildMeasureSpec() 得到的图我们可知, View 的 specSize 就是 parentSize ,这种情况下,和 match_parent 效果一样,那么怎么解决呢,就是给 View 设定一个默认的的内部宽高(mWith,mheight),并且在 wrap_content 时候设置进去就可以了 - 至于 UNSPECIFIED 情况,一般用于系统内部测量,这种情况, View 的大小就是 getDefaultSize() 的第一个参数,即getSuggestedMinimumWidth()/getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
View # getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
//如果没有设置背景那么 View 宽度就是 mMinWidth ,
//mBackground.getMinimumWidth() 得到的就是 Drawble 的原始宽度
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth,mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 的逻辑就是: 如果没有设置背景,那么 View 的宽度就是 mMinWidth ,而 mMinWidth 对应的就是Android:minWidth,如果不指定这个属性,默认为0;如果设置了背景,那么得到的就是 mMindth 和背景宽度的最大哪一个。
ViwGroup 的 measure 过程
因为 ViewGroup 是一个抽象类, 不同的 ViewGroup ,布局方式不同,测量细节也就不同的,比如 LinearLayout , RelativeLayout ,所以并没有重写 onMeaure() , 要具体实现类实现该方法。但是它提供了一个叫 measureChildren() 的方法
ViewGroup # measureChildren()
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec , heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
从代码上看, ViewGroup 在 measure 时,会对每一个子 View 进行 measure ,也就是执行 measureChild() ,这个方法也很好理解的。就是 measure 子 View 呗。
ViewGroup # measureChild()
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec , int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
//取出来子元素的LayoutParams
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 通过getChildMeasureSpec()得到创建子元素的MeasureSpec
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
//将 MeasureSpec 传递到子 view 中的measure()进行测量
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
代码里面都带有注释,很好理解,就不多说了, getChildMeasureSpec() 方法参照上面的表格就可以了 ,然后就到了child.measure(),如果这个 child 是一个 ViewGroup ,继续上的,如果是一个 View ,就执行 View 的 measure 流程。这个上面已经讲过了。
LinearLayout # onMeasure()
以 LinearLayout 为例子看一个 ViewGroup 的 measure 过程。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
代码很简单,根据不同的方向,选择不同的 measure 流程。比如选择竖直方向的 LinearLayout 的测量过程。即 measureVertical() ,源码比较长,分看来看。
LinearLayout # measureVertical()
// See how tall everyone is. Also remember max width.
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
...
//遍历每个子元素,并对每个子元素执行 measureChildBeforeLayout() ,这个方法内部调用measure()
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i , widthMeasureSpec , 0 , heightMeasureSpec , totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0);
if (oldHeight != Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
lp.height = oldHeight;
}
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
// 存储 LinearLayout 竖直方向的高度
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
if (useLargestChild) {
largestChildHeight = Math.max(childHeight, largestChildHeight);
}
}
void measureChildBeforeLayout(View child, int childIndex , int widthMeasureSpec , int totalWidth , int heightMeasureSpec , int totalHeight) {
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec , totalWidth , heightMeasureSpec , totalHeight);
}
从代码看,
- 系统会遍历子元素,并对每个子元素执行 measureChildBeforeLayout() ,然后到了 measureChildWithMargins() ,虽然不是 measureChild() ,但是看代码其实内部逻辑是一样的。在该方法内部,也会执行 View 的 measure() 方法,这样子 view 就依次开始执行 measure 过程。
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec , int widthUsed , int parentHeightMeasureSpec , int heightUsed) { final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); //得到子元素的 MeasureSpec 。显然子元素的 MeasureSpec 的创建与父容器的 MeasureSpec 和子元素本身的 LayoutParams 有关,此外还和 View 的 margin 和 padding 有关 final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + widthUsed, lp.width); final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + heightUsed, lp.height); //如果当前 child 也是 ViewGroup ,则 measure() 方法就又会调用相应的onMeasure()继续遍历它的子 View , //如果当前 child 是 View ,便根据这个 MeasureSpec 测量自己 child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); }执行某个子 View 的 measure() 后,就可以通过child.getMeasuredHeight()得到该 View 的高度,
- 通过 mTotalLength 来存储系在竖直方向的高度。每测量一个, mTotalLength 就会增加。增加的部分主要包括子 View 的高度以及子元素在竖直方向的 margin ,当子元素测量完后, LinearLayout 开始测量自己的大小。
// Add in our padding mTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom; int heightSize = mTotalLength; // Check against our minimum height heightSize = Math.max(heightSize, getSuggestedMinimumHeight()); // Reconcile our calculated size with the heightMeasureSpec int heightSizeAndState = resolveSizeAndState(heightSize, heightMeasureSpec , 0); heightSize = heightSizeAndState & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK; ... setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidthwidthMeasureSpec, childState), heightSizeAndState); if (matchWidth) { forceUniformWidth(count, heightMeasureSpec); }LinearLayout 会根据子元素的情况,来测量自己的大小。针对竖直方向而言,他的水平方向遵循 View 的测量过程。但是竖直方向则和 View 不同,具体来说
- 如果布局中高度采用的 match_parent 或者具体的值,那么它的测量过程和 View 的一致
- 如果布局高度采用 wrap_content ,他的高度就是所有子元素高度的总和,但是不能超过它父容器的剩余空间。当然还要考虑他的竖直方向的 padding ,可以参考 resolveSizeAndState() ,这是 View 的方法, LinearLayout 和 ViewGroup 都没有重新该方法
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec , int childMeasuredState) { int result = size; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); switch (specMode) { case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: result = size; break; case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: //采用 wrap_content ,他的高度就是所有子元素高度的总和,但是不能超过它父容器的剩余空间。 if (specSize < size) { result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL; } else { result = size; } break; case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: //采用的 match_parent 或者具体的值,那么返回specSize result = specSize; break; } return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK); }
看到了我们熟悉的 setMeasuredDimension() 了吗。因为 ViewGroup 中没有处理 setMeasuredDimension() ,所以还是只想到了 View 中的 setMeasuredDimension() 中 这就是 LinearLayout 的 Measure 流程,再看看 DecorView 的 Measure 过程。
DecorView #onMeasure()
因为 DecorView 是一个 Framelayout ,所以我们从 FrameLayout 开始我们的分析
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
|| MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
...
//遍历子 View ,只要 View 不是 GONE ,便处理
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
//子 View 结合父 View 的 MeasureSpec 和自己的 LayoutParams 算出子 View 自己的MeasureSpec
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec , 0 , heightMeasureSpec , 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT || lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
.....
}
FrameLayout 中的 onMeaure() 主要做两件事
- 遍历子 View ,只要 View 不是 GONE ,便会处理。
- 调用了 measureChildWithMargins() 。在 measureChildWithMargins() 里面会结合父 View 的 MeasureSpec 和自己的 LayoutParams 计算出自己的 MeasureSpce ,然后执行measure()
Activity 中得到 View 的宽高的方式
measure() 的流程就说完了,但是如果有这样一个任务,在 Activity 一启动,就想要得到 View 的宽高,这个怎么处理啊,因为 View 的 measure() 过程是和 Activity 的生命周期不是同步执行的。这样就无法保证在 Activity 执行到onStart()/onResume()的时候,能准确拿到 View 的宽高,我们可以通过下面的四种方式得到。
- onWindowFocusChanged() View 已经初始化完毕,会被调用多次,当 Activity 的窗口得到焦点和失去焦点的时候,都会执行一次,如果频繁的进行 onResume() 和 onPause() 那么 onWindowFocusChanged() 也会被循环调用
- View.post(Runnable) 通过 post 把一个 Runnable 对象加到添加队列中,然后等待 Looper 调用次 Runnable 的时候, View 已经初始化好了,
- ViewTreeObserver 使用 ViewTreeObserver 的众多回调可以完成此功能 l ,比如使用 OnGlobalFocusChangeListener 这个借口,当 View 的状态树的状态发生改变或者 View 树内部的可见性发送改变,onGlobalFocusChanged()这个方法被回调,但是需要注意,伴随 View 状态树改变,onGlobalFocusChanged()会被调用多次。
- 手动对 View 进行 measure 的宽和高。这种情况比较复杂。
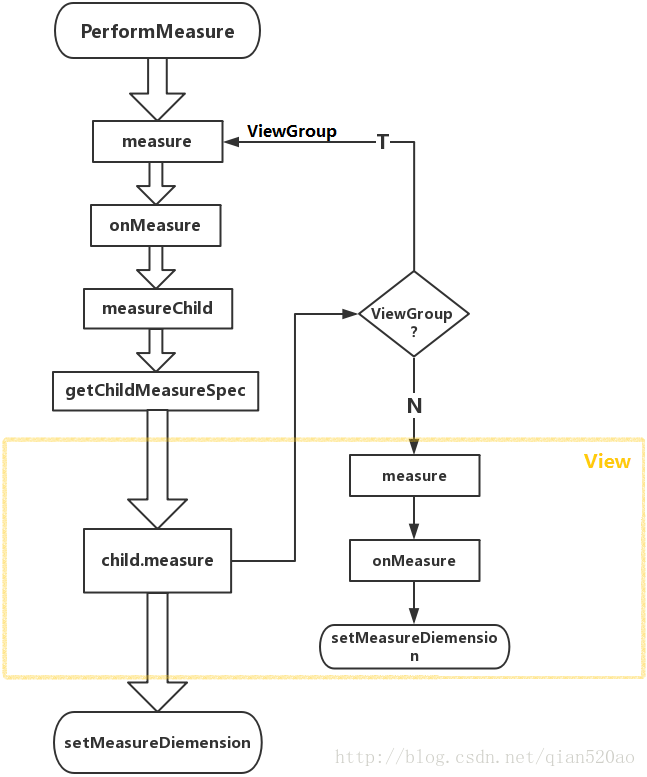
整体的流程图如下
相关文章:
View 的绘制 - 概览
View 的绘制 - Measure 流程
View 的绘制 - Layout 流程
View 的绘制 - Draw 流程, invalidate 的流程 以及 requestLayout 流程
搬运地址:
Android 开发艺术探索
既已览卷至此,何不品评一二: